It’s 11:53 PM.
You just completed a critical update that needed to go live before midnight. You’re amazing, brilliant, you did it!
You hit Publish with relief.
And then…disaster strikes.
Your browser serves up the Chrome dinosaur game — and suddenly that midnight deadline feels very, very close.
While jumping over internet cacti can be fun, the ERR_INTERNET_DISCONNECTED error when you need internet access feels like getting betrayed by the a constant presence in your life — your internet provider.
Don’t worry though; you’re not alone.
Almost everyone has had these moments, and the good news is that this is easily fixable.
Let’s get you back online!
First, What Is ERR_INTERNET_DISCONNECTED?
If you already know what’s happening, skip right to “How do you get back online?”
When browsers display the ERR_INTERNET_DISCONNECTED message, they’re telling us that our device has lost its connection to the internet.
You can think of it as a delivery truck attempting to transport packages, only to find that all the roads out are blocked.
The truck (your browser) wants to move data, but the roads (internet connection) are inaccessible. Different browsers handle the internet disconnected error differently, too.
Chrome introduces its famous dinosaur game, a playful nod to times before internet connectivity.
Microsoft Edge has a fun surfing game.

Firefox too has a cute little ping pong-styled game that can be run when the browser has no internet connection.

Safari maintains its minimalist aesthetic with a simple alert.
Despite their different presentations, each browser communicates the same fundamental problem — your device can no longer reach the internet.
Why Did You Get Disconnected?
Network connections operate through a complex chain of components working together.
If these get disrupted, the ERR_INTERNET_DISCONNECTED error shows up on your browser window.
Here’s a typical home network setup.
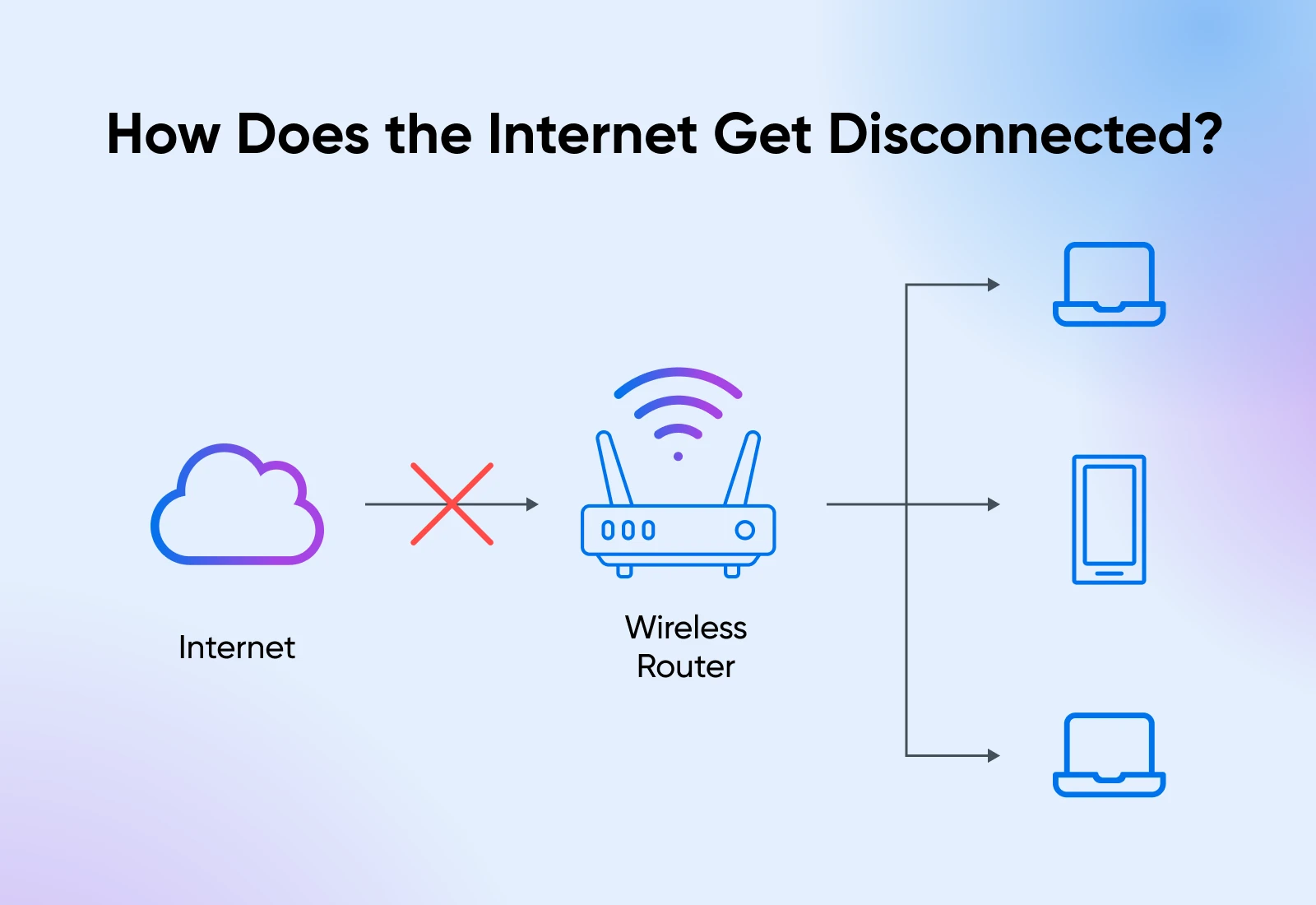
You have the WiFi router connected to the internet, and every device in your house connects to the WiFi router.
BTW, your office network is quite similar. There just are more devices and more routers working together to connect to the internet in an office setup.
There are generally two reasons why you’d get disconnected from the internet:
- Your connection to the router is broken; WiFi disconnects or the wire comes loose.
- The router’s connection to the internet (the cloud) is broken. This is generally out of your control.
Physical connection issues are often the first things you want to check. A cable might have worked itself loose during office cleaning, or for WFH folks, perhaps a pet pulled it loose.
Here’s what you need to do to get back online.
How Do You Get Back Online?
When your internet connection fails, your first instinct might be to try everything at once — unplugging cables, restarting devices, checking settings — all in rapid succession.
While this panic-driven approach is completely understandable, especially with a deadline looming, it rarely solves the problem. In fact, making random changes often creates new issues that mask the original problem.
Instead, we’ll think of it as a detective story.
Every lost connection has clues pointing to its cause, and like any good detective, we’ll examine each piece of evidence systematically.
Let’s walk through the investigation process step by step, checking each potential trouble spot until we uncover the culprit behind your disconnection.
Step 1: Assessing the Physical Infrastructure
You know that moment when your phone isn’t charging and someone asks, “Is it plugged in?”
It might seem obvious, but even the professionals sometimes overlook the simple stuff.
Walk over to your setup and follow the cables from your computer to your router. Give each cable a gentle wiggle. Sometimes they look connected but aren’t clicked in all the way.
Keep an eye on your network indicator while you do this because it might spring back to life right as you adjust the right cable!
Check the power cables next.
They tend to loosen over time, especially if your desk gets bumped occasionally. Take a quick look at each power cable for any loose connections or wear and tear (especially if you have cats– check for bite marks. I speak from experience.)
Watch for any power cables showing wear marks or unusual bending — these indicate potential points of failure requiring replacement.
Quick Fix:
Found something loose or worn?
- Push loose cables back in firmly; they should click securely.
- Test your connection after fixing each cable.
- Consider labeling the troublesome cables for future reference.
- Get IT help (or grab a new cable at home) if you spot damage.
Still offline? Let’s move to Step 2.
Step 2: Equipment Status Evaluation
Your router uses lights to tell you what’s wrong, kind of like a car’s dashboard.
The power light is your first clue: green means good, blinking suggests power problems, and no light means it’s not getting power at all.
The internet light (or WAN–Wide Area Network) is your connection indicator.

- Rapid blinking = active internet.
- Slow blinking = trying to connect.
- Solid light = might be frozen.
- No light or red light = lost connection.
Some routers have different blinking styles and light colors, which will be specified in the manual.
Quick Fixes:
- Try a different power outlet.
- Use a spare power adapter if you have one.
- Take a photo of the lights – This is really helpful for IT support.
Step 3: The Strategic Reset Process
Instead of just flipping the switch, we’ll use a much more effective method to restart your network.
This is pretty much a reboot but gives the router time to completely power down, delete all cached data from memory, and start fresh.
Here’s how:
- Document your current setup. Photograph or note your router’s position and cable connections. There’s nothing worse than unplugging everything, just to realize you have no idea where to plug it back in.
- Disconnect power from both modem and router, starting with the router.
- Wait a full 30 seconds. This critical pause allows internal components to fully discharge.
- Unplug all ethernet cables and reconnect them firmly, ensuring proper clip engagement.
- Reconnect your modem’s power supply.
- Allow exactly two minutes for modem initialization and connection establishment.
- Power up your router.
- Wait three full minutes for complete system initialization.
- Verify indicator lights show proper operation patterns.
If you’re still stuck with no internet connectivity, move on to step 4.
Step 4: Verify Connection
After completing the power cycle, systematically verify each connection layer.
Open your device’s network panel and look for your network name. If it’s missing or showing weak signal bars, try getting closer to your router.
Quick Tests:
- Try connecting with a cable if possible.
- Test with your phone to rule out computer issues.
- Check if others around you have the internet.
Here’s how you can check if your computer has connected to the network or not:
Open your device’s network settings panel. Your network should appear in the available connections list. Here’s what it looks like when my laptop is connected to WiFi, but everything else is disconnected.
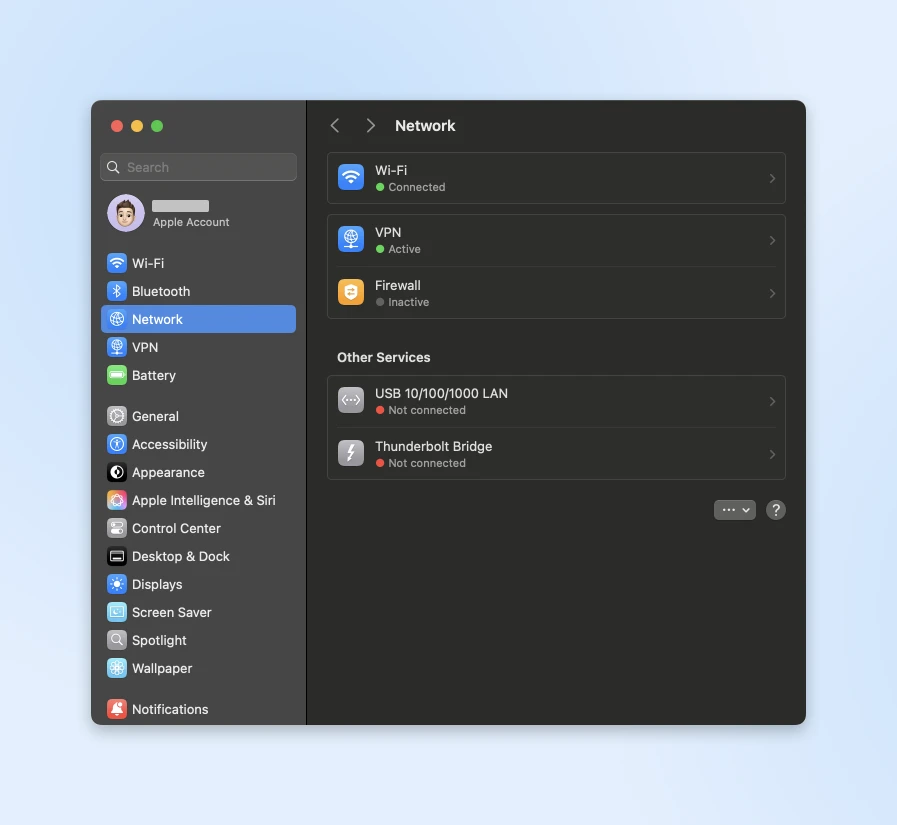
If your device isn’t picking up any networks, your router might not be broadcasting properly.
If your laptop supports it, try connecting to the internet with a wired ethernet connection. This helps rule out any wireless issues.
Also, check the WiFi signal strength with the WiFi Analyzer app; if it’s weak, you might need to reposition your router or check for interference.
You can also perform the WiFi signal strength check on your laptop with:
- Windows – WiFi analyzer
- Mac – Ultra analyzer
If you can connect with ethernet but not wireless, then you know the problem is with your wireless setup. Try connecting wirelessly from different spots and see if the signal strength changes.
Still no luck? Let’s move on to Step 5.
Step 5: Advanced Diagnostics
If nothing has worked so far, we need to dig a bit deeper. We’ll use some built-in tools to see exactly where the connection’s breaking down.
Quick Fixes:
Open Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac) and type ping 8.8.8.8 to test the internet connection:
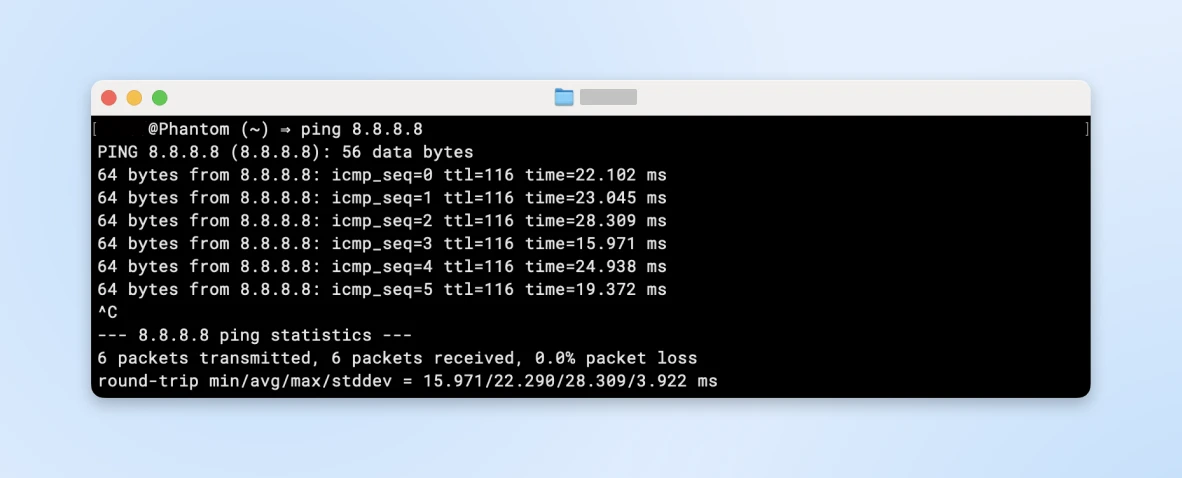
If that fails, contact your internet provider.
If it works but websites don’t, try changing your DNS to 8.8.8.8 (Google) or 1.1.1.1 (Cloudflare).
Remember: Every internet problem has a solution. If you’ve tried all the steps and still need help, don’t hesitate to call your IT support or internet provider.
They’ll appreciate knowing you’ve already tried these steps, and it will help them solve your problem faster!
Preventing Internet Disconnected Error
You need to do a few things to make sure you don’t lose your connection. Let’s look at each of these steps in more detail.
Smart Router Placement
Router placement often becomes an afterthought in busy offices.
The device gets hidden behind plants or stuffed under desks for aesthetic reasons. However, router location directly impacts video call quality, cloud file access speeds, and overall team productivity.
Remember the WiFi analyzers we talked about before? Any of those can reveal where you’re receiving the maximum network and where the WiFi strength gets weak enough to be disconnected.
You can also create a heat map of your WiFi signal.
For office setups (and even large homes), heatmaps tell you where your signal strength starts dropping so you can add WiFi repeaters, extenders, or signal boosters until you see full coverage across the area of your office.
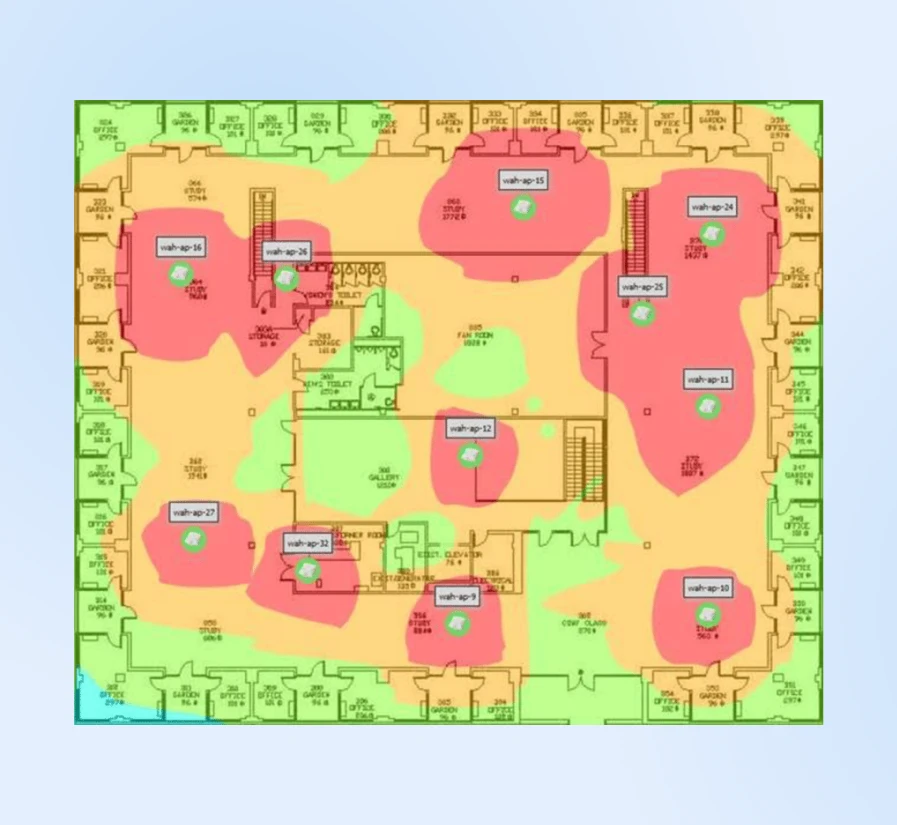
Often, moving a router just 15 feet above the ground can dramatically improve coverage. The most effective position tends to be mounted 6 feet up on a central wall, as WiFi signals travel downward in a dome shape.
But it’s less common for the router to have a consistent signal throughout its range. Common office items can disrupt WiFi signals in surprising ways:
- Microwave ovens can disrupt 2.4GHz signals.
- Cordless phones may share frequency bands.
- Metal filing cabinets create signal shadows.
- Neighboring networks compete for bandwidth.
Find ways to isolate this interference or strengthen your WiFi signal by placing more devices on the floor.
Create a Maintenance Schedule
Just as vehicles need regular maintenance, network infrastructure requires consistent attention. Your IT department probably has this on lockdown, but here’s an example of what a maintenance schedule would look like, so you can appreciate all their hard work:
- Monthly checks should occur during off-peak hours, typically early in the morning before regular business operations begin.
- Run speed tests from every department.
- Clear dust from equipment (compressed air works wonders).
- Check cable connections (they loosen over time).
- Update network documentation.
- Quarterly assessments provide opportunities for deeper system evaluation.
- Comprehensive speed testing with detailed mapping.
- Equipment inspection (looking for wear signs).
- Review and update emergency contact lists.
- Team training refreshes on basic troubleshooting.
- Firmware management deserves special attention. Outdated firmware can lead to major outages, while proper tracking and testing of updates helps maintain stable performance.
- Track firmware versions in a shared spreadsheet.
- Review update notes before installing.
- Test updates on backup equipment first.
- Keep detailed logs of performance changes.
Backup Connections Planning
A robust backup strategy protects businesses from costly interruptions. Here’s how you can think about planning your backup connections:
- Primary connection: Maintain a business-class internet service with guaranteed service levels and priority support. Also, create direct contact with service provider technical support to avoid customer service channels during outages.
- Backup systems: Along with this, we’d recommend having a secondary cable connection from a different provider for redundancy.
- Mobile hotspots: If keeping a secondary connection active costs too much at your business stage, mobile hotspots can do the job just fine considering how fast mobile internet is these days. But keep running trials every few weeks with all your internet out and just the mobile hotspots to ensure people on the team can handle an outage.
- Emergency response: Create detailed procedures for connection failures:
- Diagnostic steps for common problems.
- Contact information for support services.
- Alternative workspace arrangements.
- Customer communication templates.
A final resort would be to stay connected with local co-working spaces as emergency workspaces when needed for business continuity.
Documentation and Training
Technical documentation should be clear and actionable.
A centralized guide containing network diagrams, equipment information, and troubleshooting steps helps staff resolve common issues independently.
Maintain comprehensive network documentation such as:
- Network topology diagrams.
- Equipment specifications and warranties.
- Configuration backups.
- Maintenance logs.
- Update histories.
Train team members on basic troubleshooting procedures. Create quick-reference guides for common issues. Clear escalation procedures help staff identify when to handle issues themselves and when to seek additional support.
More Than Just Connection Problems
While we’ve focused on internet disconnection errors, you might run into several other errors that prevent access to websites.
Sometimes your browser and server just aren’t speaking the same language.
Each of these guides walks you through fixing the problem step by step. Bookmark them for those moments when things aren’t working quite right — they’ll help you get back on track quickly!
- The 400 Bad Request Error pops up when something’s wrong with how your browser asks for information — maybe a mistyped URL or some cookie problems.
- You might also see ERR_CONNECTION_RESET when your connection drops mid-conversation with the server. These connection hiccups can be particularly frustrating when you’re in the middle of important work.
- Form submissions can be especially tricky. Ever filled out a long form only to lose everything when you hit submit? That’s often related to ERR_CACHE_MISS Errors. They’re particularly annoying when trying to save important information or make a purchase.
- WordPress users face their own set of challenges. The “Maximum Execution Time Exceeded” message might appear when trying to install a new plugin, or you could run into WordPress image upload issues while updating your site’s media library.
- Sometimes the problem lies within the server itself. A 504 Gateway Timeout means the server’s taking too long to respond, while a 503 Service Unavailable error suggests it’s too busy or down for maintenance. These server issues usually resolve themselves, but our guides can help you understand what’s happening and what you can do about it.
Ready for Any Internet Adventure
Network problems never arrive at convenient times. That dinosaur game might be fun, but not when you’re facing a critical deadline or in the middle of an important task.
The key isn’t avoiding every possible problem but knowing what to do when they occur.
Keep this guide handy, save your ISP’s number somewhere offline, and know that every connection issue has a solution.
And when in doubt, explore our guides on common website errors and management tips.
Sign up for our newsletter to be notified about new tutorials when they’re published. We may not be able to every internet hiccup, but we can sure help you handle them like a pro.